The Distinction Between Standard CNC Lathes and Swiss Turning
In the realm of precision machining, where every millimeter counts and accuracy is paramount, the choice between standard CNC lathes and Swiss turning can significantly impact the outcome of a manufacturing process.
While both methods share the goal of shaping raw materials into precise components, they diverge in their approach and application. Understanding the distinction between standard CNC lathes and Swiss turning is not merely an exercise in technical differentiation but a gateway to optimizing efficiency, quality, and ultimately, the success of manufacturing endeavors.
What is Swiss Turning
Swiss turning, also known as Swiss-style machining or Swiss screw machining, is a specialized method of precision machining renowned for its ability to produce intricate and high-precision components with exceptional accuracy and efficiency.
Originating in Switzerland in the late 19th century to manufacture precision watch components, Swiss turning has evolved into a versatile machining technique utilized across various industries including aerospace, medical devices, electronics, and automotive.
At the heart of Swiss turning lies the Swiss-type lathe, a machine distinguished by its unique design and operational principles. Unlike conventional lathes, Swiss-type lathes feature a sliding headstock and a guide bushing that provides unparalleled support and stability for small-diameter workpieces.
>>> Read more: Everything You Need to Know About Swiss Screw Machining
This setup enables the machining tool to make precise cuts very close to the guide bushing, resulting in minimal vibration and superior dimensional accuracy.
One of the hallmark features of Swiss turning is its capability to efficiently machine long, slender, and complex parts in a single operation. This is achieved through the integration of multiple cutting tools, often including live tooling and sub-spindles, which allow for simultaneous machining of multiple surfaces and features.
Additionally, Swiss turning excels at handling tough materials such as stainless steel, titanium, and high-temperature alloys, making it ideal for manufacturing critical components with stringent dimensional and surface finish requirements.
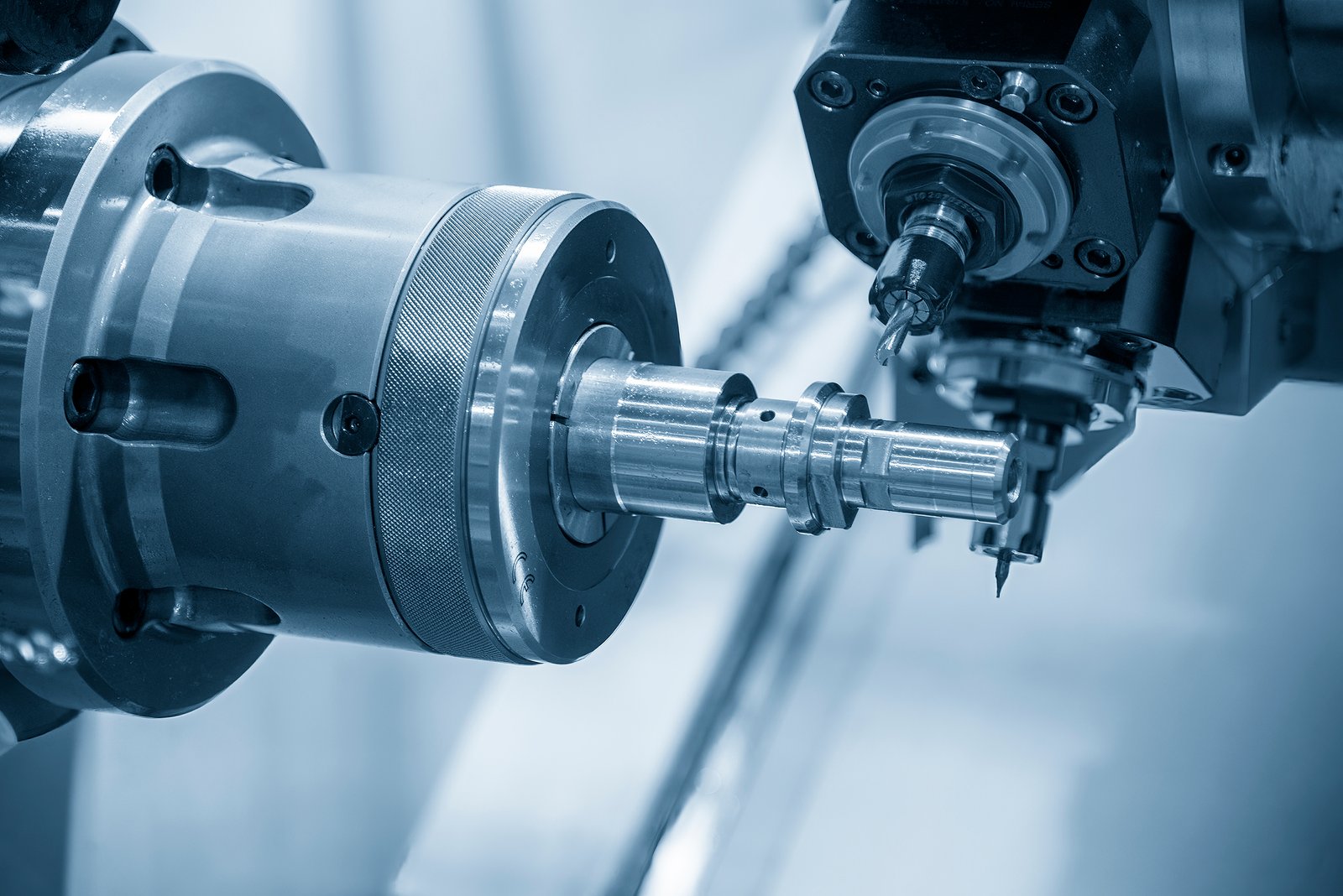
Standard CNC Lathes
Standard CNC lathes, also known as conventional or traditional CNC lathes, are foundational machines in the realm of machining, playing a vital role in the production of a wide array of components across various industries. These lathes utilize computer numerical control (CNC) technology to automate the machining process, allowing for precise shaping and finishing of raw materials such as metal, plastic, and wood.
Unlike Swiss turning, standard CNC lathes typically feature a stationary headstock and a movable carriage that holds the workpiece. This configuration allows for versatile machining operations including turning, facing, drilling, threading, and more. Standard CNC lathes are well-suited for machining components of varying sizes and shapes, from simple cylindrical parts to more complex geometries.
>>> Read more: What is CNC Turning? Advantages of CNC Turning
One of the key advantages of standard CNC lathes is their flexibility and adaptability to a wide range of manufacturing tasks. Operators can program these machines to perform specific machining operations with high precision and repeatability, making them indispensable in mass production as well as prototyping environments.

The Distinction Between Standard CNC Lathes and Swiss Turning
The distinction between standard CNC lathes and Swiss turning lies in their approaches to subtractive machining processes, each offering unique advantages and capabilities.
Swiss lathes, akin to conventional turning centers, execute subtractive machining operations with precision. However, they employ movable headstocks to secure the workpiece, allowing for dynamic repositioning along the Z-axis during machining. This mobility, coupled with lateral support from a guide bushing, ensures that machining operations are consistently executed in close proximity to a stable support point.
The utilization of movable headstocks and guide bushings in Swiss lathes serves a crucial purpose: minimizing deflection and vibrations within the workpiece. This enables Swiss lathes to excel in the production of elongated cylindrical parts and components, a feat often challenging for conventional CNC turning lathes.
On the other hand, conventional CNC turning centers adopt a different approach. These machines typically clamp the workpiece at one or both ends, depending on the part size and lathe configuration. Operating at high speeds reaching several thousand rpm, the lathe “turns” the workpiece while precision-guided cutting and grinding tools, controlled by CNC programming, meticulously remove material according to custom part designs.
Through subtractive manufacturing, conventional CNC turning lathes efficiently transform raw materials into precision-machined components or assemblies by removing unnecessary material.
While lacking the dynamic repositioning capabilities of Swiss lathes, standard CNC turning lathes remain invaluable tools for a wide range of machining tasks, offering reliability, efficiency, and versatility in the manufacturing process.
Cam-operated screw machines, while advanced for manual machining, come with drawbacks. They require highly specific procedures, leading many shops to specialize in operating just one machine, limiting manufacturing flexibility.
Both Swiss CNC machines and cam-operated screw machines feed bars in and out of the spindle along the Z-axis, like conventional lathes. However, CNC Swiss lathes stand out due to their integration of CNC technology.
They use computer-generated toolpaths from CAD files and are controlled by G-Code (CAM) files, allowing precise execution of various machining features, from contouring to threading, with versatility and accuracy.
In contrast, cam-operated screw machines rely on mechanical cams and custom forming tools, synchronized through a timing cam system. Achieving accuracy across different setups often requires manual adjustments and specialized knowledge, making them less adaptable than CNC Swiss lathes.

Conclusion
The distinction between standard CNC lathes and Swiss turning lies in their unique approaches to subtractive machining processes. Standard CNC lathes offer reliability, efficiency, and versatility, making them indispensable tools for a wide range of machining tasks.
Meanwhile, Swiss turning excels in precision and is particularly well-suited for producing elongated cylindrical parts with minimal deflection and vibrations. Both methods have their strengths and limitations, and the choice between them ultimately depends on the specific requirements of the manufacturing process.
However, by understanding the capabilities of each approach, manufacturers can make informed decisions to optimize efficiency, quality, and overall success in their machining endeavors.

