CNC Turning and CNC Milling are two types really important in CNC Machining industries. Each other has strength, processing and applications individually. Today, Let’s explore are the Differences between CNC Turning and CNC Milling with MaTec Vietnam
CNC Turning Process
The CNC Turning process begins by securing a round workpiece onto a spindle.
Typically, the spindle is held in place by a chuck with three jaws, although alternative methods such as using a faceplate or positioning the workpiece between centers can also be employed.
The rotation of the spindle imparts motion to the workpiece.
Fixed Cutting Tool
In contrast to the movement of the workpiece, the cutting tool used in this process remains stationary, mounted in a turret. This fixed position of the cutting tool provides the stability necessary for precise metalworking.
Single-point Cutting Tool
CNC turning operations commonly utilize a single-point cutting tool. These tools are adept at accurately shaping and forming the desired patterns on the rotating workpiece.
Continuous Chip Formation
As the CNC Turning operation progresses, the cutting action typically results in the formation of continuous chips. These chips are a natural byproduct of the metal removal process, indicating effective machining.
Two-axis Tool Movement
To achieve the desired shapes or designs on the workpiece, the cutting tool moves along two axes.
The Z-Axis controls the rotation of the spindle or adjustments in diameter, while the X-Axis regulates the size of the workpiece.
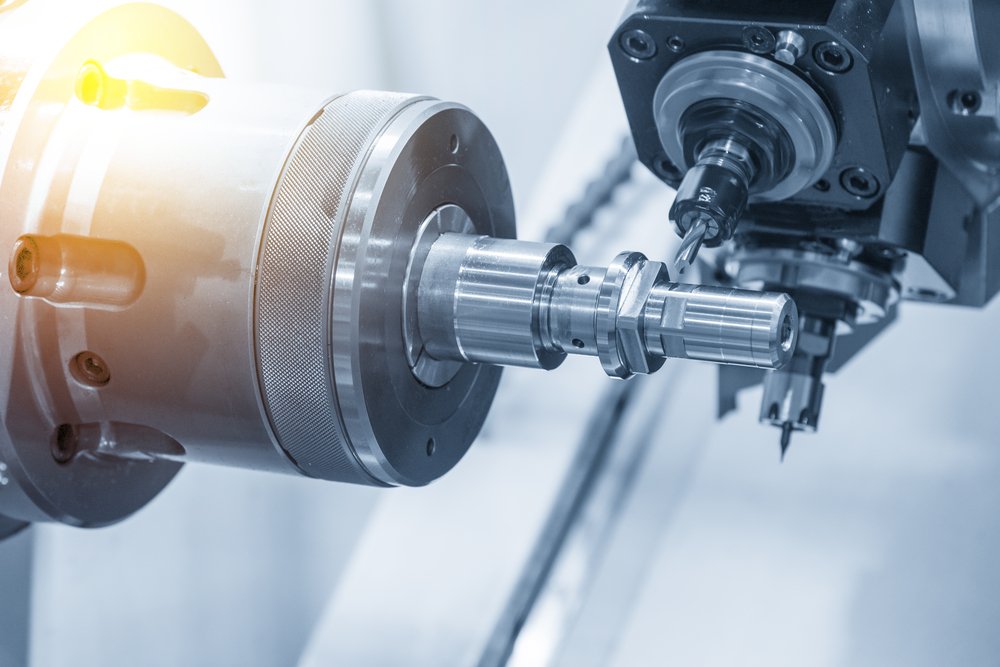
Application in Cylindrical Workpieces
CNC Turning processes are crucial for manufacturing items with cylindrical or tubular shapes.
The precision with which this process handles cylindrical workpieces makes it invaluable in industries such as automotive and aerospace.
Hydraulic Clamping
Securing the workpiece onto a rotating spindle requires robust clamping to ensure accurate machining results.
Given the forces exerted by the workpiece during machining, hydraulic clamping is commonly employed.
This method enhances stability and control throughout the turning process.
>>> Read more: What is CNC Turning? Advantages of CNC Turning
CNC Milling Process
In CNC milling operations, the workpiece is typically secured in one of three ways for stability.
It can be clamped to the machine table, held in a vice, or fixed in a fixture. Simultaneously, the cutting tool is precisely mounted in the turret quill on the spindle. Once this setup is complete, the spindle begins rotational motion.
Utilization of Multipoint Cutting Tools
Milling operations primarily employ multipoint cutting tools. The choice of tool depends on the specific profile to be machined. Various tools are available for different applications – including end mills, face mills, slitting cutters, and ball nose cutters, each offering its own advantages depending on the task at hand.
Formation of Segmented Chips
Unlike turning, the milling process generates segmented chips due to the cutting action. These short, fragmented chips are typically easier to manage and dispose of, thus promoting a cleaner and safer work environment.
Milling of Rectangular Workpieces
A distinguishing feature of CNC milling operations is the ability to machine rectangular or prismatic workpieces. This capability makes it a preferred process for industries requiring components with such geometries.
>>> Read more: What is CNC Milling? How does CNC milling work?
Pneumatic Clamping of the Cutting Tool
Aligned with the requirements of CNC milling operations, the cutting tool is mounted in the turret quill on the spindle.
The clamping pressure required is lower compared to turning operations, allowing for pneumatic clamping. Consequently, the tool is securely held in place during machining, with reduced demands on holding force, leading to increased tool longevity and operational efficiency.
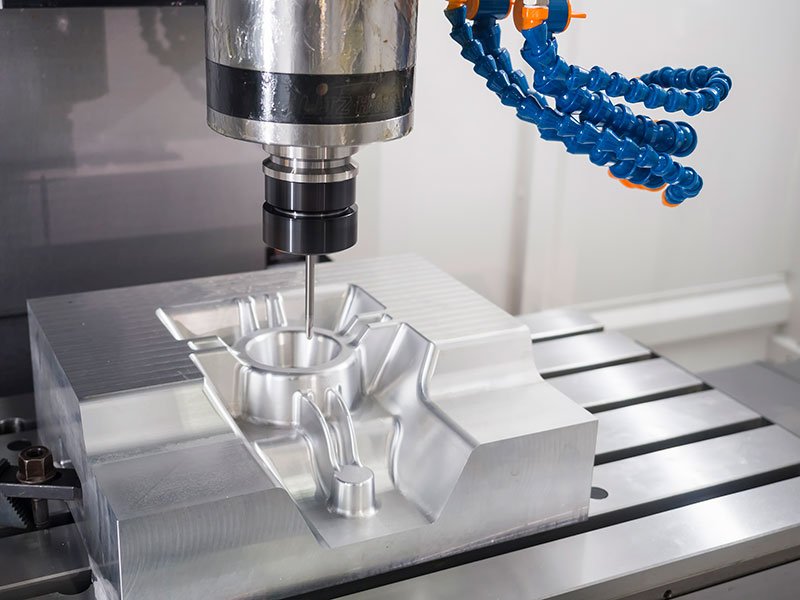

CNC Turning and CNC Milling Operations
Both CNC Turning and CNC Milling are prominent subtractive manufacturing processes, each with distinct operations.
CNC Turning involves the rotation of a workpiece along two axes while two cutting tools move along two axes to precisely shape cylindrical forms.
On the contrary, CNC Milling utilizes stationary workpieces while multiple cutting tools move along three axes to carve intricate three-dimensional shapes. These processes find diverse applications across numerous industries for creating precision parts.
CNC Turning Process
CNC turning begins by securing the workpiece onto a rotating spindle controlled by the CNC program, which adjusts its speed based on manufacturing requirements.
As the workpiece rotates, a cutting tool follows a path parallel to the axis of rotation, removing material according to the design plans stored within the software.
This precise rotational operation enables the creation of cylindrical or conical parts with exceptional accuracy and repeatability.
Parts Produced through CNC Turning
CNC turning machining is extensively used for producing components such as shafts, bolts, and bushings due to its capability to generate smooth rounded profiles. These parts play a crucial role in various applications, ranging from automotive to electronics industries, underscoring its significance.
CNC Milling Process
CNC Milling distinguishes itself from turning by maintaining the workpiece stationary while rotating at high speed. It moves along multiple axes at various positions simultaneously, employing multiple cutting tools whose positions, angles, and depths are controlled via software instructions to remove material and shape parts as required. Multi-axis operation further enhances flexibility and versatility in this milling process.
Milling Complex Shapes with CNC
The flexibility of CNC Milling enables it to produce a wide array of shapes on flat or irregular surfaces, ranging from simple flat parts to intricate features like pockets, slots, or contours. Industries spanning from art to mechanics heavily rely on CNC Milling due to its broad applicability.
Understanding the achievable shapes and geometries through CNC Turning and CNC Milling is essential when determining the most cost-effective method for producing precise parts.
Achieving Shapes with CNC Turning
CNC Turning excels in producing cylindrical or conical shapes. As the workpiece rotates on its spindle, CNC-programmed cutting tools systematically and consistently remove material, making it ideal for crafting shafts, tubes, and discs that require symmetrical geometry around a central axis. This makes CNC Turning an excellent solution for numerous industrial applications.
Versatility of CNC Milling: Shapes, Pockets, Slots, and Contours
CNC Milling is renowned for its versatile application in creating various shapes and features. The multi-axis movement of its cutting tool allows it to approach a workpiece from different angles, a capability not attainable with CNC Turning.
From basic forms like flat surfaces and rounded edges to intricate contours such as pockets within workpieces, slots in narrow openings, and contours on complex profiles, CNC Milling’s operational flexibility makes it the preferred process across diverse industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics manufacturing.

Workpiece Orientation
The orientation of the workpiece is crucial in both CNC Turning and CNC Milling processes, as it determines the unique geometries and characteristics of the finished products due to the distinct movement of the workpiece in these processes.
Workpiece Orientation in CNC Turning
In CNC Turning, the workpiece is mounted onto a spindle that rotates at a speed set by its CNC program. This spindle can be positioned horizontally or vertically, depending on the machine setup.
The rotational axis of the workpiece serves as the central axis around which turning operations are performed.
Utilization of Cutting Tools in CNC Turning
CNC Turning involves the use of cutting tools that move almost linearly along the rotating workpiece, following its X and Z axes. These tools meticulously carve away material with precision to shape the workpiece as desired.
Workpiece Orientation in CNC Milling
In CNC Milling, the workpiece remains stationary throughout the processing, unlike in CNC Turning.
The orientation of the workpiece can be either horizontal or vertical, depending on the type of milling machine being used. Once secured on the milling table, it remains stable during the operation.
Movement of Cutting Tool in CNC Milling
CNC Milling employs a cutting tool that moves along multiple directions, following an X, Y, and Z axis path. This tool rotates and shifts in various ways to approach the workpiece from different angles and depths, enabling the creation of shapes with intricate geometries such as pockets, grooves, and contours in the finished part.
Application of CNC Turning and CNC Milling Technologies
CNC Turning and CNC Milling processes are widely applied due to their precision. Parts manufactured through these processes are prevalent across industries, spanning from aerospace and automotive to electronics and consumer goods.
Common Parts Produced with CNC Turning
CNC Turning is particularly adept at fabricating parts with round or cylindrical shapes, such as shafts, hubs, bushings, wheels, and pulleys.
The precision and efficiency of CNC Turning make it the preferred method for producing components for manufacturing, automotive engineering, aerospace, or consumer electronics applications.
Versatility of CNC Milling in Part Production
CNC Milling offers remarkable flexibility to manufacturing processes. With multi-axis operation, it can manufacture parts with intricate geometries, including flat surfaces, grooves, slots, contours, and 3D shapes, with ease.
From delicate jewelry or decorative elements with elaborate designs to essential mechanical parts featuring curves and slots, CNC Milling finds applications across sectors such as aerospace, automotive manufacturing, electronics, medical manufacturing, and beyond.
Its extensive range of applications establishes CNC Milling as one of the most versatile manufacturing processes available today.

Tools Utilized in CNC Turning and CNC Milling Operations
The precision and efficiency of CNC Turning and CNC Milling processes are heavily reliant on the cutting tools utilized. Each cutting tool performs distinct operations that significantly impact the outcome of these manufacturing processes.
Types of Cutting Tools Used in CNC Turning
CNC Turning commonly employs single-point cutting tools featuring specialized profiles tailored to produce specific shapes on workpieces as required.
Various tool shapes are utilized, including straight turning tools, curved turning tools, facing tools, and threading tools, each offering distinct capabilities and applications.
Cutting Tools Employed in CNC Milling Systems
CNC Milling utilizes a diverse array of cutting tools, each selected according to its intended function.
End mills are employed for profile milling and contouring, while drill bits facilitate drilling operations, and slot drills create slots in metal surfaces.
Additional tools include face mills, ball-nose cutters, and others specializing in specific functions to meet the requirements of various milling tasks.
Machining Direction
CNC Turning and CNC Milling exhibit numerous differences, including the manner in which their cutting tools traverse their designated paths. This variance significantly impacts the complexity of shapes achievable through each process.
Radial Movement in CNC Turning
In CNC Turning, the cutting tool moves radially in relation to the workpiece, following an axis parallel to its rotation. This radial movement enables precise shaping of the material into cylindrical forms.
Multidirectional Movement in CNC Milling
On the other hand, CNC Milling utilizes cutting tools capable of traversing along multiple axes simultaneously, including the X, Y, and Z axes. This multidirectional movement empowers CNC Millers to fabricate intricate geometries such as pockets, grooves, and contours that cannot be achieved with the radial movement employed in CNC Turning.

Choosing Between CNC Turning and CNC Milling
CNC Turning is optimal for manufacturing parts with symmetrical profiles along a central axis, such as shafts, tubes, or cones. Conversely, CNC Milling’s multidimensional movement excels in crafting intricate geometries like slots, pockets, contours, or complex three-dimensional shapes.
Selecting the suitable CNC process hinges on several criteria related to project requirements.
Shape, complexity, quantity, material, and precision specifications all hold significant weight.
Opting between CNC Turning and CNC Milling involves aligning these factors with the respective strengths of each process to achieve successful, cost-effective manufacturing outcomes.
CNC Turning and CNC Milling offer distinct capabilities in modern machining.
Turning is adept at creating cylindrical parts, while Milling is proficient in shaping intricate geometries. The choice between the two processes depends on factors such as the shape, complexity, and precision demands of the part at hand.
CNC Turning is most suitable for cylindrical components, whereas CNC Milling is better suited for parts with intricate or unconventional features.
Both processes play indispensable roles across various manufacturing industries. These advanced CNC techniques facilitate the production of diverse parts, underscoring the versatility and adaptability of modern machining.
Conclusion
Overall, the distinction between CNC Turning and CNC Milling lies in their respective methods of material removal and tool movement. While CNC Turning revolves around rotating workpieces and linear tool movement, CNC Milling employs stationary workpieces and multi-directional tool movement.
Understanding these differences is crucial in selecting the most suitable machining process for your specific needs.
If you require manufacturing services in either of these fields, don’t hesitate to reach out to MaTec Vietnam for swift assistance and quotations.
As a leading CNC Machining manufacturer in Vietnam with over 10 years of experience exporting to markets in the US and Europe, MaTec Vietnam takes pride in delivering top-notch solutions tailored to your requirements.

