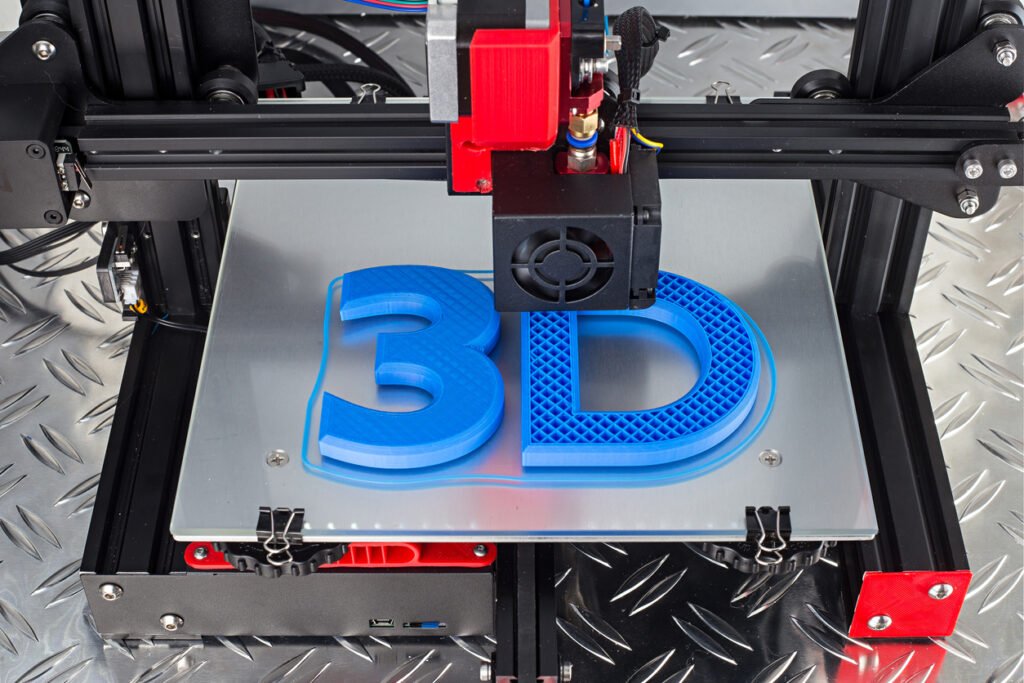
In the rapidly evolving world of manufacturing, two technologies stand out for their ability to produce intricate and precise parts: 3D printing vs CNC machining. While both methods aim to create high-quality components, they operate on fundamentally different principles. 3D printing, an additive process, builds objects layer by layer from a digital file, offering unparalleled design flexibility.
On the other hand, CNC machining is a subtractive process that shapes parts by removing material from a solid block using precision tools. Understanding the key differences between these two methods is crucial for selecting the right technology for your manufacturing needs.
This article, MaTec Vietnam will delves into the specifics of 3D printing vs CNC machining, comparing their advantages, limitations, and ideal applications.
What is 3D Printing?
3D printing is a collection of processes that share a common approach to manufacturing. This technique involves creating virtual models of three-dimensional parts, which are rendered by software as a series of slices. The thickness of these slices is tailored to the specific machine or setting being used. Each layer is printed sequentially, and the stacking and bonding of these slices enable the construction of a complete part from these finite 2D steps.
Various materials can be used in 3D printing, including extruded polymer filaments, light-sensitive resins, laser-melted powders, filament feedstock, waxes, and even biological materials. To achieve a successful print, several tools must work together, including a CAD package to design the part and save it as an STL file, slicer software to convert the 3D file into a sequence of 2D machine instructions, and the 3D printer itself.
The first commercially viable 3D printing systems emerged in the late 1980s, and since then, the technology has rapidly expanded in both methods and materials. Compared to CNC machining, 3D printing offers better cosmetic finishes and more efficient material usage. It also eliminates the need for direct manual labor in producing complex parts.
What Benefits Does 3D Printing Offer Over CNC Machining?
Speed of Production
3D printing can produce net shape parts quickly, without the need for extensive setup or manual programming, which is typically required for CNC machining.
Cost Efficiency
3D printing is generally more cost-effective for creating complex net shapes. It involves minimal setup and operational intervention, often making CNC components up to ten times more expensive than 3D printed parts.
Ease of Use
Modern 3D printers are becoming more office-friendly and require only modest skills for setup and maintenance. They are increasingly capable of meeting a wide range of needs. In contrast, CNC machining remains a heavy-engineering process that requires highly skilled operators and ongoing training to maintain proficiency.
What Are the Cons of 3D Printing Compared to CNC Machining?
Material Strength
3D printing processes can result in varied material strengths compared to the native properties of the materials. For instance, Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) in ABS may achieve as low as 10% of the material’s ultimate tensile strength (UTS), while Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) in nylon can achieve up to 100%. In contrast, CNC machining produces parts from solid, undisturbed materials, typically resulting in higher strength.
Dimensional Accuracy
While 3D printing can achieve good dimensional accuracy, it may struggle with high precision requirements. CNC machining, on the other hand, is highly precise and can attain improved accuracy by adjusting the processing speed.
Surface Finish
3D printing often faces challenges with surface finish due to process mechanics, particularly Z-resolution, which can cause stepped surfaces and visual imperfections. CNC machining produces parts with a uniform and highly precise surface finish, provided that cutter paths are well-programmed for smooth results.

What is CNC Machining?
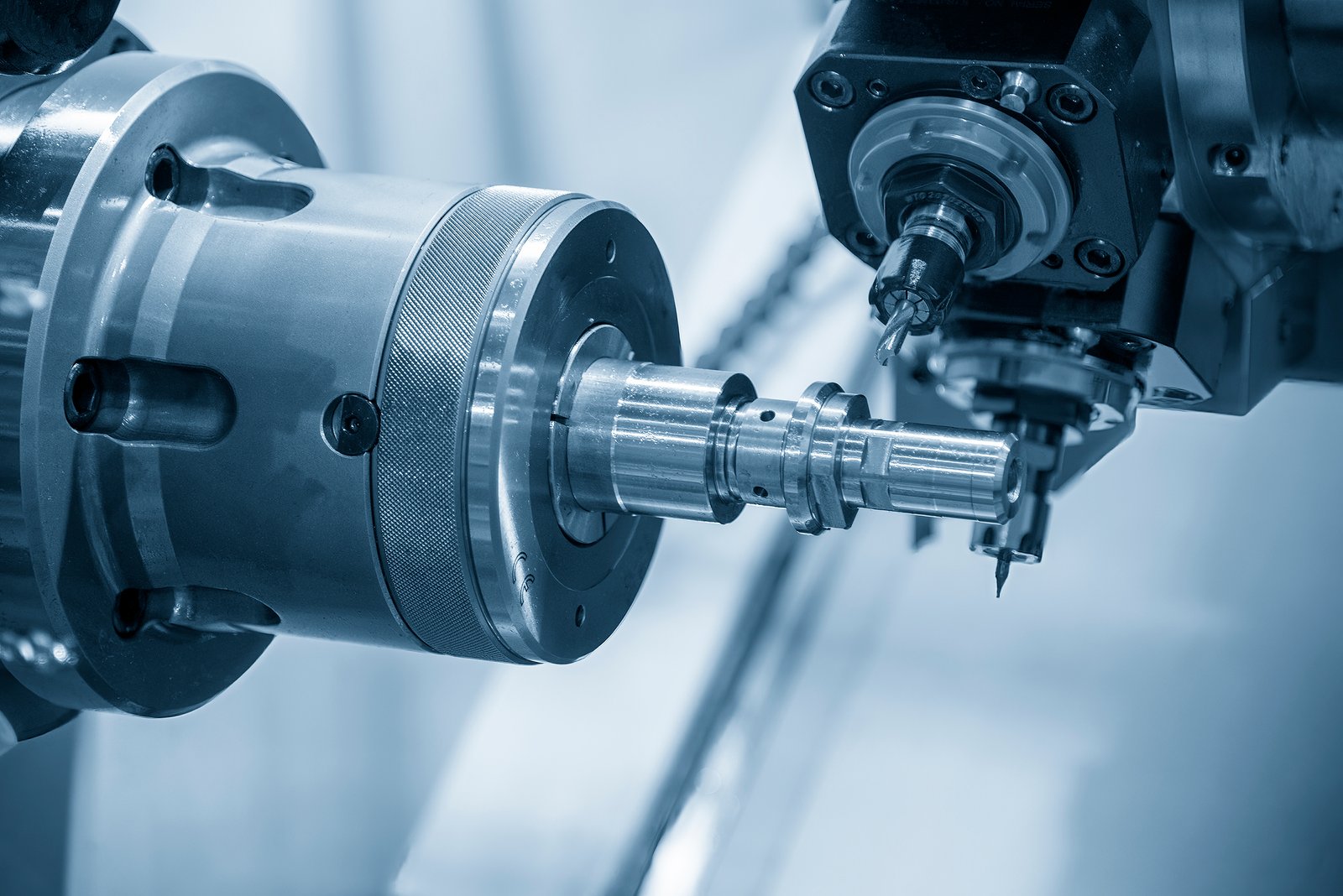
CNC machining is a computerized manufacturing process that uses pre-programmed software and codes to control the movement of machine tools. This technology employs a variety of complex machinery, such as lathes, mills, and grinders, to accurately and precisely cut, create, and shape different parts.
The first CNC machine was developed by James Parson in 1949, focusing on producing helicopter and aircraft blades. In 1958, Richard Kegg and MIT introduced the first CNC milling machine.
Though CNC machining involves a complex setup and can be costly, it is preferred for parts that require long-term wear properties, strength, smooth surface finish, and high precision, making it superior to 3D printing in these aspects. Figure 2 below illustrates an example of a CNC milling machine.
Read more: What is Precision Machining?
What Are the Pros of CNC Machining Compared to 3D Printing?
Material Integrity
CNC machining uses engineering materials in their undisturbed, native state, ensuring that parts retain the full properties of these materials. In contrast, 3D printing often utilizes materials that are weaker approximations of their traditional counterparts.
Precision
CNC machining produces parts with higher precision, as it can maintain tighter tolerances compared to the tolerances achievable with 3D printing.
What Are the Cons of CNC Machining Compared to 3D Printing?
Tooling Requirements
CNC machining often necessitates the creation of mounting tools, complicating the setup process. In contrast, 3D printing allows for the creation of free-floating parts built directly on a table or scaffold, simplifying production.
Material Waste
CNC machining is a subtractive process that removes excess material, resulting in significant waste. Conversely, 3D printing is an additive process that minimizes waste by using only the material necessary to build the part.
What is The Difference Between 3D Printing vs CNC Machining
| Attribute | 3D Printing | CNC Machining |
| Material Availability | Limited | Unlimited |
| Design Flexibility | Not constrained by process limitations | Limited by cutting capabilities, tool access, tool paths, minimum radius defined by axes, and repositioning needs |
| Precision | Varies from 0.016 to 1 mm+, typically around 0.2 mm | High precision at 0.005 mm, achievable with slow feed rates, new cutting tools, and shallow cuts |
| Operator Skill | Generally low | Very high |
| Build Speed | Low setup time but builds often take hours | Potentially high setup and programming time; cutting phase is very fast |
| Surface Finish | Grainy, rough, and stepped; features often blurred | Can achieve very high-quality surface finish with longer cutting times |
| Strength | Typically 10-20% of the native material | Generally 100% of the native material |
| Cost | Assumed cost is $X | Generally $5X to $10X |
Frequently Asked Questions
How does the speed of 3D printing compare to CNC machining?
Preparing for the printing of a 3D component involves minimal setup time before printing can commence. While the printing process itself may be slow by some standards, most prints are likely to be completed within a few hours and ready for use.
On the contrary, CNC machining necessitates skilled preparation, involving programming for cutter selection and path. It often requires the use of custom or modified jigs to secure the part during processing, which may include repositioning.
This preparation phase can consume significant time before the first cut. However, the cutting process is generally swift, and complex parts can typically be finished in an hour or less of actual machining. The total time required for preparation and machining may extend to a day or more, depending on the complexity of the part.
How do the lead costs of 3D printing vs CNC machining compare?
CNC machining incurs significant programming and setup expenses, making it notably pricier compared to 3D printing—often five to ten times the cost.
However, in scenarios where a series of prototypes with minor adjustments is needed, the setup cost for modified CNC-cut parts will be considerably lower. In contrast, each subsequent 3D printed part will cost the same as the initial one.
How do 3D printing vs CNC machining compare in terms of volume production?
When the significant setup effort can be distributed across multiple parts, CNC machining can yield more cost-effective results compared to 3D printing. 3D printing offers fewer volume advantages, as each part incurs the same material and machine costs regardless of volume.
How do the materials used in 3D printing compare to those used in CNC machining?
In terms of material selection and ensuring the attainment of material properties, CNC machining offers superior options. Essentially, CNC allows for the utilization of a wide range of engineering materials, extending to the spark-erosion CNC machining of pre-hardened tool steels. CNC-machined parts retain the inherent properties of the raw material, largely unaffected by the machining process.
In contrast, the selection of materials for 3D printing is constrained by the specific processes supported by each technology. The construction methods inherent to certain 3D printing technologies impose significant limitations on the attainment of desired properties.3D-printed parts often suffer from weaknesses stemming from factors such as anisotropic grain formation, porosity, inadequate layer bonding, and the utilization of printable but non-engineering materials.
Conclusion
Overall, this article’s comparison between 3D printing vs CNC machining underscores the distinct advantages and limitations of each manufacturing method. While 3D printing excels in design flexibility, rapid prototyping, and minimal material waste, CNC machining offers superior precision, material integrity, and cost-effectiveness for high-volume production runs.
The choice between these technologies depends on various factors, including the specific requirements of the project, desired material properties, budget constraints, and production volume.